First demonstration of Real-Time Brain Mapping in a Web Browser
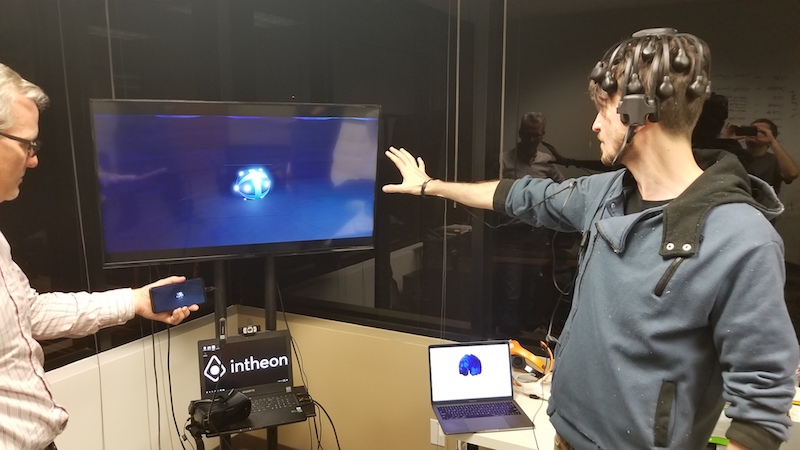
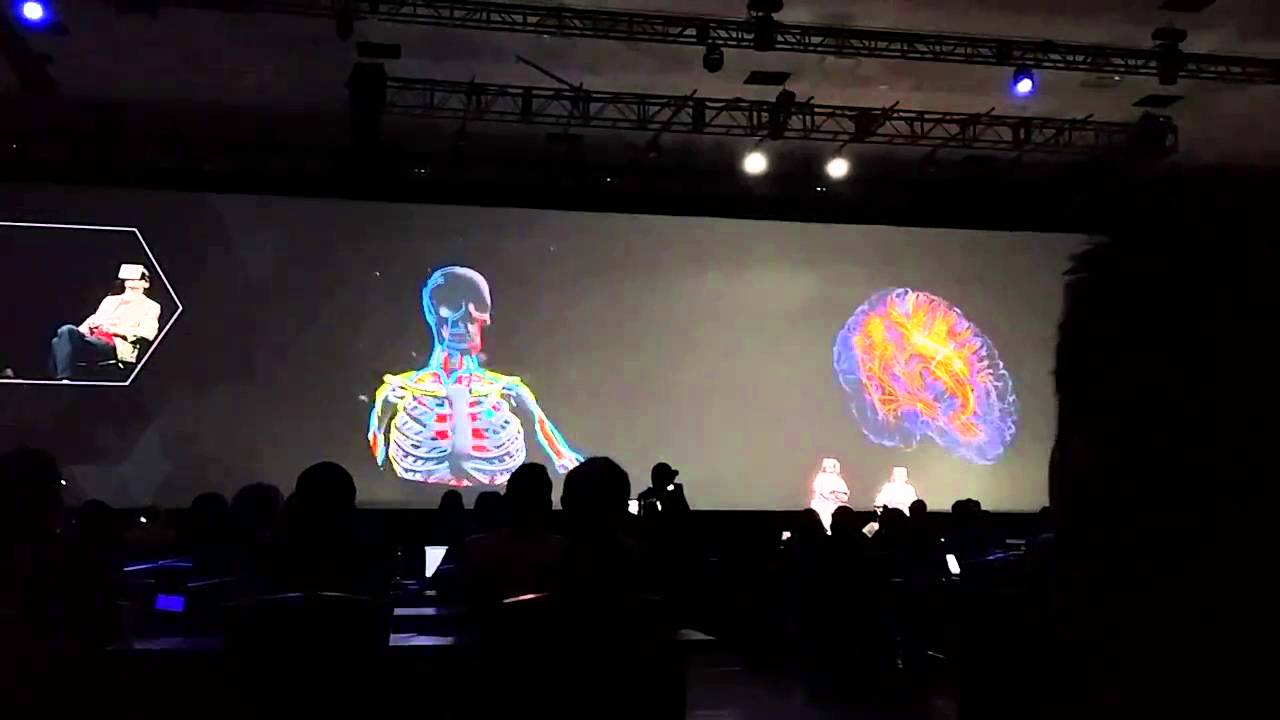
This clip shows the first demonstration of wireless dry EEG brain activity mapping and directed connectivity analysis with real-time interactive 3D visualization in a standard web browser on a smart phone. This represents an important step towards enabling powerful new pervasive applications of EEG, including live remote monitoring of brain activity (neurotelemetry) for clinical or consumer applications.
Here, Intheon CTO Christian Kothe (left) wears the Cognionics “Quick-20″ 19-channel dry wireless EEG system, while CEO/CSO Dr. Tim Mullen (right) navigates his brain on a smartphone. All computation is carried out in real-time on the NeuroScale cloud platform. The lightweight web application is built on the NeuroScale API, utilizing just one of numerous possible pipelines for neuroimaging, biosignal processing, brain-computer interfacing, and cognitive state assessment.
NeuroScale is the world’s first cloud API platform enabling developers to easily integrate state-of-the-art neurotechnology into any internet-enabled application. Anytime, anywhere.
Interested? Apply for the Beta program at www.intheon.io !
Technical Stuff
In this example, we demonstrate the most famous of brain rhythms: localized 8-12 Hz alpha (posterior dominant rhythm) power and cortical network activity when the subject closes and opens eyes. Increased alpha activity is associated with blocking of input to sensory cortex. However, it is also associated with various states of consciousness and utilized extensively in neurofeedback. When closing eyes, we expect prominent increases in activity localized to the occipital (visual) cortex.
Here brain electrical activity is mapped to the cortex using a smoothly distributed source reconstruction algorithm with subsequent power spectral estimation. Frequency-domain cortical network connectivity is estimated using Multivariate Spectral Granger Causality between user-defined cortical regions of interest including major hubs of the “task negative / default mode network” and “task positive network”. The size of a connection between two regions, as well as ball size, denotes the amount of information transfer between regions. Warm colors indicate increased brain activity and connectivity.
Science!
Relevant scientific publications by Intheon members:
- Mullen, T., Kothe C., Chi. M., Ojeda, A., Kerth, T., Makeig, S., Jung, T-P., Cauwenberghs, G. (2015). Real-time Neuroimaging and Cognitive Monitoring Using Wearable Dry EEG. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. Special Issue on Wearable Technologies. 2015 Nov;62(11):2553-67.
- Mullen, T. R. (2014). The dynamic brain: Modeling neural dynamics and interactions from human electrophysiological recordings. University of California. (Order No. 3639187)
- Makeig, S., Kothe, C., Mullen, T., Bigdely-Shamlo, N., Zhang, Z., Kreutz-Delgado, K (2012). Evolving Signal Processing for Brain-Computer Interfaces. Proceedings of the IEEE , vol.100, no.Special Centennial Issue, pp.1567-1584.
Tags: Brain Connectivity, Brain Mapping, Mobile Neuroimaging, NeuroScale, Neurotelemetry, Wearable EEG, Web Visualization, Video